Enjoy ‘AI slop’ summer. What’s coming next is worse
Welcome to AI Decoded, Fast Company’s weekly newsletter that breaks down the most important news in the world of AI. You can sign up to receive this newsletter every week here. “AI Slop” summer is here AI image and video generation tools have gone mainstream, with millions creating content and using them on platforms like TikTok and YouTube. Social networks such as Facebook and Pinterest are also seeing a surge in AI-generated posts. Meta is actively promoting this trend, as AI content is easy to produce and often drives higher engagement, creating more opportunities to sell ads. Much of the AI-generated content is what critics call “AI slop”—low-quality material often produced by low-wage workers in developing countries aiming to harvest clicks on platforms like YouTube, Facebook, and TikTok. This content frequently spreads further via messaging apps like WhatsApp and is often political in nature. One growing genre features right-wing fantasy videos portraying acts of revenge or defiance by MAGA figures such as Donald Trump or Pam Bondi. These are typically just still images with overlaid text—clearly fictional. (Left-leaning versions exist too, though they more often rely on real footage, such as Jamie Raskin or Jasmine Crockett dismantling Republican talking points in Congress.) AI-generated content is also increasingly surfacing in search results, often pushing aside higher-quality human-created material. E-commerce platforms like Amazon are flooded with AI-generated product descriptions, user reviews, and even entire books. Some news organizations have started publishing AI-written articles, especially in sports and news roundups—many riddled with inaccuracies. Recently, the Chicago Sun-Times and The Philadelphia Inquirer unintentionally ran book list inserts featuring AI-generated descriptions of books that don’t actually exist. Right now, much of the AI-generated content online can still be distinguished from genuinely human-made material. Take, for example, a viral AI video from April that depicted overweight U.S. factory workers (a satire of Trump’s tariff policies). It looked fairly realistic but still gave off that unmistakable “generated” vibe. Still, the line is blurring fast. Consider the recent viral clip of an Australian woman trying to pass airport security with her “service kangaroo.” It racked up over a million likes before it was revealed to be AI-generated. Some viewers saw through it—many did not. The video proved that with a semi-plausible premise and decent AI tools, the boundary between real and fake can dissolve entirely. It’s not hard to see where this is going. Google’s new Veo 3 video generation tool is a case in point: The sample videos are alarmingly realistic. Time recently showed how these tools can create convincing deepfakes of political riots and election fraud. AI-generated content has been advancing for years, but we may have arrived at a moment where even video—once the hardest medium to fake—can no longer be trusted. With more powerful tools and social platforms eager to boost engagement, we’re likely heading toward a web saturated with AI-generated content. And when anything can be fake, everything becomes suspect. Are we ready for the “zero-trust” internet? Reddit sues Anthropic over AI training data The social platform Reddit says the AI company Anthropic has used content created by Reddit users to train AI models in ways that violate its policies. In a lawsuit filed Wednesday in a San Francisco court, Reddit accused Anthropic of using users’ posts without permission, causing harm to the platform. AI companies rely heavily on information stores like Reddit to train the large language models that power popular chatbots such as ChatGPT and Anthropic’s Claude. Reddit is seen as a particularly valuable resource because it holds millions of human-to-human conversations across thousands of topics, spanning the past two decades. The conversations are not only valuable for their content, but for how authentically they reflect the way people write and speak. No wonder Reddit cofounder and CEO Steve Huffman calls it “the most human place on the internet.” And content licensing for AI training is a big and growing business for the platform. Reddit’s shares on the New York Stock Exchange finished the day up more than 7% after news of the lawsuit broke Wednesday. The company has already formed content licensing agreements with Google and OpenAI (Sam Altman is a major shareholder in Reddit). It’s possible that the lawsuit was filed after Reddit and Anthropic failed to come to terms on a content licensing agreement. Reddit certainly isn’t the first content company to sue a well-funded AI lab for alleged misuse of data. OpenAI, Perplexity, Google, and others have all been the target of legal actions related to training data. Many of these cases center on the question of whether or not data that’s publicly available on the internet falls under th

Welcome to AI Decoded, Fast Company’s weekly newsletter that breaks down the most important news in the world of AI. You can sign up to receive this newsletter every week here.
“AI Slop” summer is here
AI image and video generation tools have gone mainstream, with millions creating content and using them on platforms like TikTok and YouTube. Social networks such as Facebook and Pinterest are also seeing a surge in AI-generated posts. Meta is actively promoting this trend, as AI content is easy to produce and often drives higher engagement, creating more opportunities to sell ads.
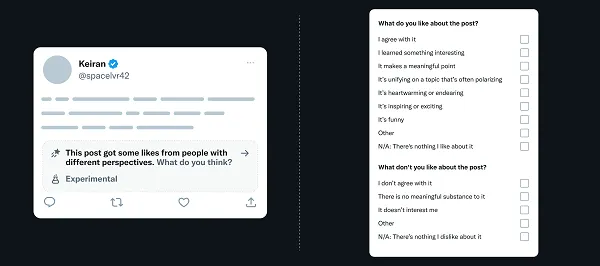
Much of the AI-generated content is what critics call “AI slop”—low-quality material often produced by low-wage workers in developing countries aiming to harvest clicks on platforms like YouTube, Facebook, and TikTok. This content frequently spreads further via messaging apps like WhatsApp and is often political in nature. One growing genre features right-wing fantasy videos portraying acts of revenge or defiance by MAGA figures such as Donald Trump or Pam Bondi. These are typically just still images with overlaid text—clearly fictional. (Left-leaning versions exist too, though they more often rely on real footage, such as Jamie Raskin or Jasmine Crockett dismantling Republican talking points in Congress.)
AI-generated content is also increasingly surfacing in search results, often pushing aside higher-quality human-created material. E-commerce platforms like Amazon are flooded with AI-generated product descriptions, user reviews, and even entire books. Some news organizations have started publishing AI-written articles, especially in sports and news roundups—many riddled with inaccuracies. Recently, the Chicago Sun-Times and The Philadelphia Inquirer unintentionally ran book list inserts featuring AI-generated descriptions of books that don’t actually exist.
Right now, much of the AI-generated content online can still be distinguished from genuinely human-made material. Take, for example, a viral AI video from April that depicted overweight U.S. factory workers (a satire of Trump’s tariff policies). It looked fairly realistic but still gave off that unmistakable “generated” vibe. Still, the line is blurring fast. Consider the recent viral clip of an Australian woman trying to pass airport security with her “service kangaroo.” It racked up over a million likes before it was revealed to be AI-generated. Some viewers saw through it—many did not. The video proved that with a semi-plausible premise and decent AI tools, the boundary between real and fake can dissolve entirely.
It’s not hard to see where this is going. Google’s new Veo 3 video generation tool is a case in point: The sample videos are alarmingly realistic. Time recently showed how these tools can create convincing deepfakes of political riots and election fraud. AI-generated content has been advancing for years, but we may have arrived at a moment where even video—once the hardest medium to fake—can no longer be trusted.
With more powerful tools and social platforms eager to boost engagement, we’re likely heading toward a web saturated with AI-generated content. And when anything can be fake, everything becomes suspect. Are we ready for the “zero-trust” internet?
Reddit sues Anthropic over AI training data
The social platform Reddit says the AI company Anthropic has used content created by Reddit users to train AI models in ways that violate its policies. In a lawsuit filed Wednesday in a San Francisco court, Reddit accused Anthropic of using users’ posts without permission, causing harm to the platform.
AI companies rely heavily on information stores like Reddit to train the large language models that power popular chatbots such as ChatGPT and Anthropic’s Claude. Reddit is seen as a particularly valuable resource because it holds millions of human-to-human conversations across thousands of topics, spanning the past two decades. The conversations are not only valuable for their content, but for how authentically they reflect the way people write and speak. No wonder Reddit cofounder and CEO Steve Huffman calls it “the most human place on the internet.”
And content licensing for AI training is a big and growing business for the platform. Reddit’s shares on the New York Stock Exchange finished the day up more than 7% after news of the lawsuit broke Wednesday. The company has already formed content licensing agreements with Google and OpenAI (Sam Altman is a major shareholder in Reddit). It’s possible that the lawsuit was filed after Reddit and Anthropic failed to come to terms on a content licensing agreement.
Reddit certainly isn’t the first content company to sue a well-funded AI lab for alleged misuse of data. OpenAI, Perplexity, Google, and others have all been the target of legal actions related to training data. Many of these cases center on the question of whether or not data that’s publicly available on the internet falls under the “fair use” safe harbor of the Copyright Act, rendering it fair game for AI training.
Trump’s foreign student ban: a master class in the art of the self-own
Secretary of State Marco Rubio said last week that the U.S. will begin revoking visas for visiting Chinese students, including those in “critical fields,” and will tighten visa requirements for future applicants. The Trump administration repeatedly claims it wants America to win the global AI race, while being openly hostile to the very brains that could help the U.S. achieve that goal.
Research from the National Foundation for American Policy shows that two-thirds (66%) of U.S.-based AI startups have immigrant cofounders, and 55% of billion-dollar startups were founded or cofounded by immigrants. Meanwhile, other countries are rolling out the red carpet. The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology offered guaranteed admission to any Harvard international student. Germany and Ireland are courting current and prospective Harvard students. China, too.
As AI impacts talent needs, foreign students will be needed to fill demand. Because AI coding assistants are significantly increasing the productivity of individual engineers, big tech companies are investing less in entry-level programmers (and more in GPUs and data centers). CEO Satya Nadella says 20% to 30% of Microsoft code is now AI-generated, and that he expects that rate to grow to 95% by 2030. Tech companies will likely need people with PhDs or other graduate-level degrees to fill more specialized roles such as those responsible for training and steering AI models.
And that talent pool isn’t big enough. International graduate students with advanced technical skills are more valuable than ever. The Administration is signaling a retreat from the global competition for AI talent.
More AI coverage from Fast Company:
- With its Samsung deal, Perplexity could be headed to the big leagues
- Jeffrey Katzenberg bets big on AI video ads with his investment in Creatify
- How to use AI to find your next job
- Music giants begin negotiating AI licensing rights for labels and artists
Want exclusive reporting and trend analysis on technology, business innovation, future of work, and design? Sign up for Fast Company Premium.